Vitamin B12 is one of eight B vitamins necessary to maintain the shape of our bodies. For the building of red blood cells, the metabolism of nutrients, and our immune system, a water-soluble B12 vitamin is required. We can get it from foodstuffs like beef, fish, poultry, and milk products, fortified foods, dietary supplements, and prescription medicines, as our body does not make B12. You can also get Vitamin B-12 Shots.
How much Vitamin B12 is needed?
In Canada, a regular Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) is 2.4 mcg, 2.6 mcg, and 2.8 mcg for most adults. However, Health Canada states that 10–30 percent of the people over 50 years of age are not able to ingest as much vitamin B12 from foods as they require. So they have to take vitamin B12 supplements.
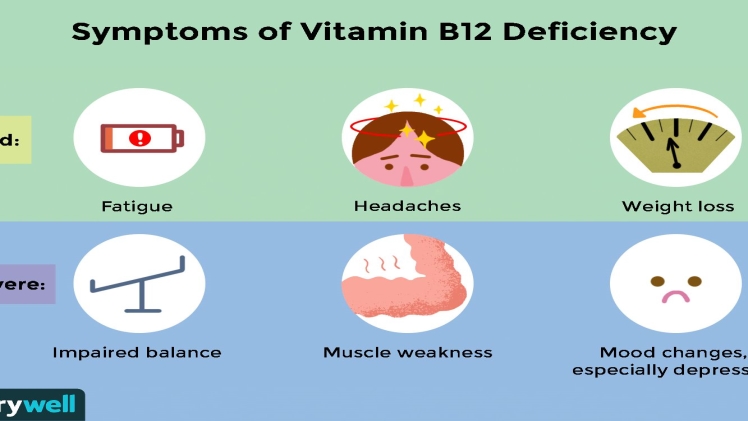
A deficiency continues to form when we do not get any vitamin B12. As the signs of a B12 vitamin deficiency gradually occur and vary, they are often ignored. Anemia, lack of appetite, constipation, confusion, numbness, and tingling can be included in our hands and feet. A B12 deficiency will lead to lifelong problems of neurology and blood disorders if left untreated. It is also essential that you receive sufficient vitamin B12.
Can anybody at risk for vitamin B12 deficiency?
The vitamin B12 deficiency can be caused by insufficient absorption or taking a drug that interferes with the absorption of this vitamin in your diet. Older people who have unhealthy diets, pernicious anemia, or malabsorption conditions, or impaired cognitive function disorders, Deficiency is more prevalent in those people. The status of your B12 can be seen by a quick blood test.
What are vitamin B12 supplements?
The only option could be to take a B12 supplement for someone who has trouble consuming B12, or who lacks this nutrient in their diet. It is important to be aware that there are several different B12 supplements and an informed choice is important. Let us explore the distinctions.
Various forms of B12 have varying bioavailability levels (amount of vitamin absorbed and ready to use). The active and inactive forms of vitamin B12 are available. The two types of vitamin B12 are mostly used: methyl alcoholamine and cyanocobalamine. Some new formulas also include a third form, dibencozide.
Both methylcobalamin and dibencozide are the bioavailable bio-coenzymed forms of vitamin B12 that are used by our bodies effectively. Even with genetic differences that hinder the absorption of B vitamins, they have immediate, direct nutrient support.
Read More About: f95zone